
Save your image in TIFF format (or as JPEG, maximum quality).If applicable please re-label your artwork with a font supported by Elsevier and ensure it is an appropriate font size.The tonal areas of the image should be in RGB mode for color (preferably), or grayscale for black-and-white halftone images.
#Pixel vs vector image software#
The only way to do this is by combining the properties of the two image types, and this normally results in files that are larger.Ĭombination (line and halftone) artwork should comply with the following requirements regardless of the software and hardware used in the process. The requirements for this particular type of image are that the text is as clear as possible, with unchanged quality of the halftone. The most common occurrences are images where the labelling of the image is outside of the halftone area, or where there is a graph next to the halftone area. This is an image type that is a combination of both a halftone (gray or/and color) and line art elements: combination artwork.
#Pixel vs vector image full#
In computing, a grayscale image is an image in which the value of each pixel is a single sample, that is, it carries the full (and only) information about its intensity. Grayscale images have many shades of gray in between. Grayscale images are distinct from black-and-white images, which in the context of computer imaging are images with only two colors, black and white. Line weights range from 0.10 pt to 1.5 pt.No data should be present outside the actual illustration area.Always include/embed fonts and use the recommended fonts where possible: Arial, Helvetica, Courier, Times, Times New Roman, Symbol.Always include a preview/document thumbnail.MS Office documents are treated as hybrid vector artwork by Elsevier. Most drawing programs offer an EPS "Save As.
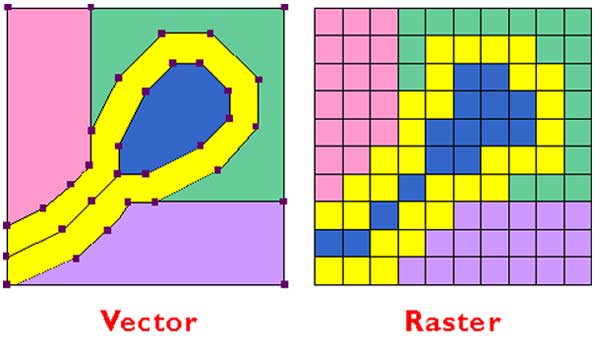
Such a hybrid vector image can, for instance, be created in MS PowerPoint, when you import an image (bitmap) and then annotate that image with text, lines and arrows. Hybrid vector images are annotated bitmap images like photographs. Such images are typically graphs, bar charts, chemical formulae, and plots (pure vector images, and resolution independent). Vector graphics formats are complementary to raster graphics (images as an array of pixels, like photographs).Ī vector image does not use pixels in images but mathematical expressions (e.g., "draw a line with this color and thickness between these two coordinates").


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
